An important component that manages routes and containers.
Review previous parts of this series for better understanding:
This is fourth part of the Kubernetes series. In this part I will try to add more insights into Kubernetes Service.
What is a Service in Kubernetes?
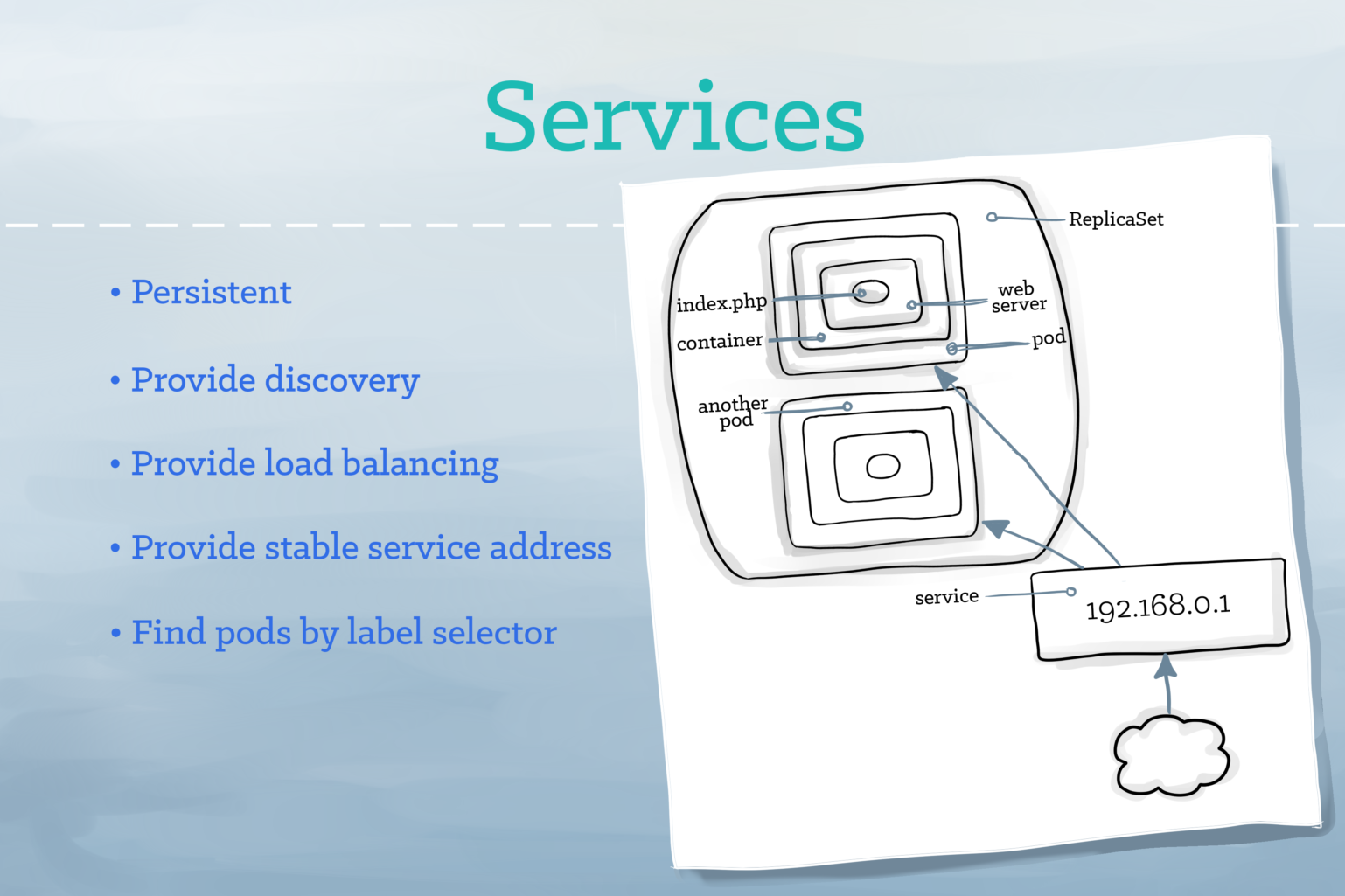
A Service groups Pods together that perform the same function as a single entity. It keeps track of containers in the Pods and routes to the containers for internal and external access. A Service’s IP address remains stable regardless of changes to the Pods it routes to, which makes it easy to gain discoverability and can simplify containers designs. By default, Services are only available using an internally routable IP address, they can be made available outside of the Cluster by choosing one of several strategies.
Types Of Services
There are 4 types of Services, specified by the type field in the Service Configuration File:
ClusterIPis the default, which grants the Service a stable internal IP accessible from anywhere inside of the cluster.NodePortconfiguration works by opening a static port on each node’s external networking interface. Traffic to the external port will be routed automatically to the appropriate pods using an internal cluster IP service. This will expose your Service on each Node at a static port, between 30000-32767 by default. When a request hits a Node at its Node IP address and the NodePort for your service, the request will be load balanced and routed to the application containers for your service.LoadBalancercreates an external load-balancer to route to the service using a cloud provider’s Kubernetes load-balancer integration. TheCloud Controller Managerwill create the appropriate resource and configure it using the internal service service addresses. This will create a load balancer using your cloud provider’s load balancing product, and configure a NodePort and ClusterIP for your Service to which external requests will be routed. Creating LoadBalancer for each Deployment running in the cluster will create a new cloud load balancer for each Service, which can become costly.Ingress Controlleris used to manage routing external requests to multiple services using a single load balancer.ExternalNameallows to map a Kubernetes Service to a DNS record. It can be used for accessing external services from Pods using Kubernetes DNS.
Review
Services are the essential parts of Kubernetes which provides secure communication mechanism with in the Kubernetes infrastructure.
I will share about Kubernetes Controller next.